Agribusiness Services
Value Chain Analysis

Agribusiness services represent a critical component of Hawai'i Island's agricultural sector, providing essential support to farms and agricultural enterprises of all sizes. These services encompass a wide range of functions that are crucial for the efficient operation, growth, and sustainability of the island's agricultural businesses. The primary purpose of focusing on this grouping of services is to enable HIAP's members to better understand the support systems that underpin the agricultural value chains, the market ecosystem that facilitates these services, and the potential for enhancing the competitiveness and resilience of Hawai'i Island's agricultural sector. By identifying and addressing systemic constraints in the provision and accessibility of these services, this analysis aims to promote sustainable growth and increased productivity amongst our members.
Click on any of the components of the Agribusiness Services value chain analysis below to explore the details.
System Terms & Definitions
Title | Definition |
|---|---|
Crowding In | The process in which other market actors replicate or adopt successful interventions, leading to broader market transformation. |
Economic Clusters | Geographic concentrations of interconnected businesses, suppliers, service providers, and institutions that collaborate to improve productivity, innovation, and competitiveness. |
Horizontal Linkages | Relationships and connections among businesses or organizations at the same level of the value chain (e.g., farmer cooperatives or industry associations). |
Interventions | Strategic actions designed to address constraints, unlock opportunities, and improve overall system performance. Successful interventions stimulate market-driven growth without creating dependency. |
Market Actors | Individuals, businesses, organizations, or institutions involved in producing, processing, trading, or regulating products and services within a market system. |
Market Systems | A framework that looks at the broader environment in which market actors (farmers, businesses, consumers) operate, including policies, institutions, and support services that shape their interactions. |
Market Systems Development (MSD) | An approach to economic development that seeks to create sustainable and inclusive markets by addressing the underlying constraints and incentives that shape market behaviors. |
Market Systems Facilitation | A strategy that enables market actors to take ownership of solutions, by encouraging partnerships, improving information flow, and aligning incentives to drive market development. Facilitators avoid taking over market functions and instead enable existing actors to succeed. |
Scaling Up | Expanding the reach and impact of an intervention by integrating it into mainstream business practices, government policies, or institutional frameworks. |
Systems Change | A fundamental shift in the way market systems operate, resulting from improved relationships, services, and market conditions that sustain long-term growth and resilience. |
Value Chains | The full range of activities and actors involved in bringing a product from production to final consumption, including input suppliers, farmers, processors, distributors, and retailers. |
Vertical Linkages | Relationships between different levels of the value chain, such as between farmers and buyers, or processors and retailers. |
Agribusiness Services Market System Map
The market system map provides an overview of the various functions, rules and stakeholders of the agribusiness services value chain. This helps to understand the various inter-relationships and interdependencies that shape performance and opportunities for service providers to improve the availability and quality of services to producers. Click on any of the System Components below to see the underlying information or review the data summaries below the system map.






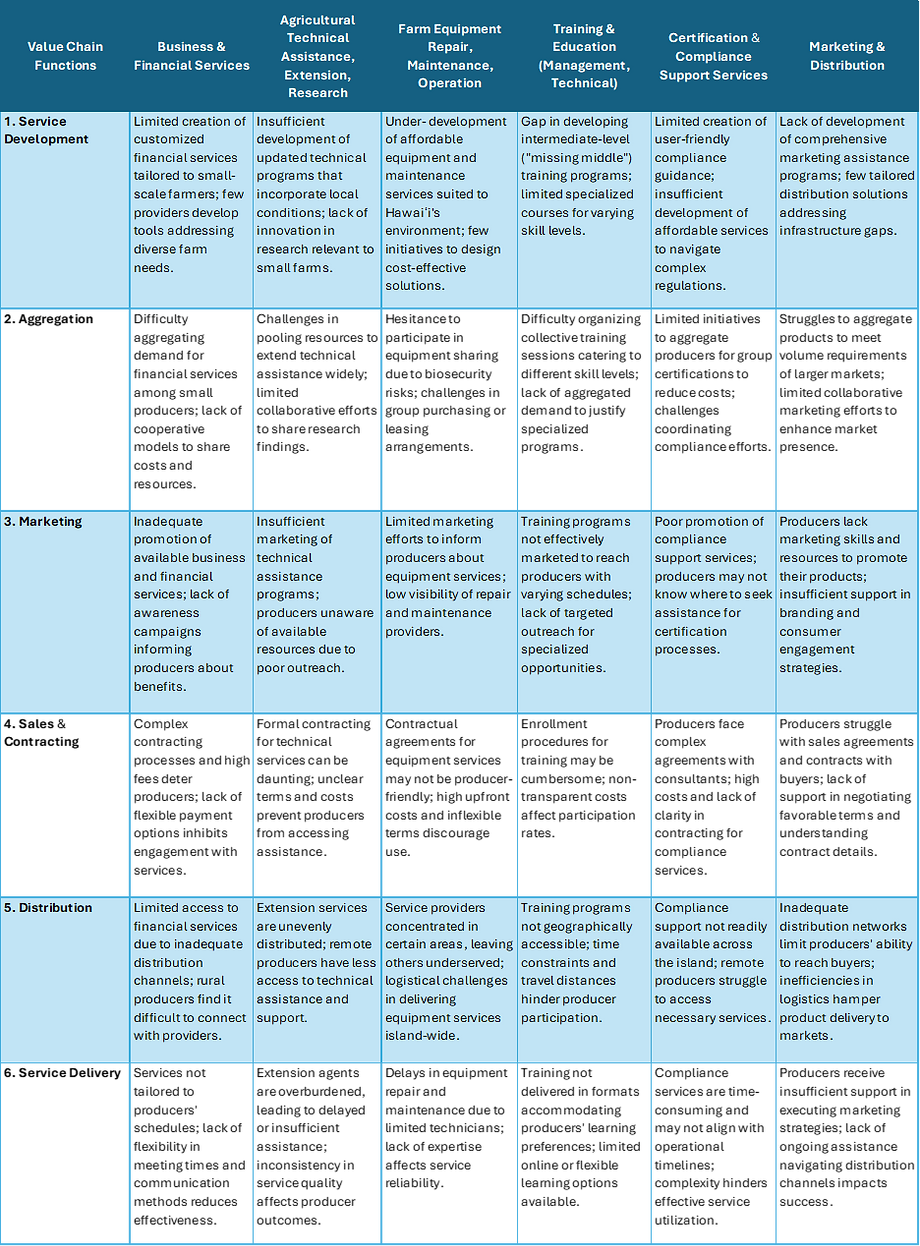
Core Value Chain Functions
Value Chain Data Summary



The agribusiness services value chain diagram below illustrates the relationships and flows between service providers and producers within Hawaiʻi Island's agricultural market system. It highlights how various entities interact through core value chain functions to support the agricultural sector to improve productivity, profitability, and sustainability for producers of staple food and export commodities.

Core Value Chain Functions
-
Service Development involves creating and designing agribusiness services that cater to the specific needs of Hawaiʻi Island's producers. This function encompasses the identification of producer needs, development of tailored solutions, and continuous improvement of services. Service providers—such as agricultural consultants, educational institutions, and research organizations—are primarily responsible for this function.
-
Aggregation refers to the consolidation of services, resources, or producers to achieve greater efficiency and economies of scale. In the agribusiness services value chain, this function can involve bundling multiple services into comprehensive packages or coordinating groups of producers for collective benefits. Entities like cooperatives, producer associations, and brokers often play key roles in aggregation. They facilitate access to shared services such as bulk purchasing of inputs, group training sessions, or collective marketing efforts, enhancing value and reducing costs for individual producers.
-
Marketing involves promoting agribusiness services to producers to raise awareness and encourage uptake. This function encompasses advertising, outreach campaigns, informational events, and communication strategies that highlight the benefits and value of the services offered. Both service providers and intermediaries—such as industry associations, extension agents, and cooperatives—can engage in marketing efforts.
-
Sales/Contracting is the process through which producers engage with service providers to procure agribusiness services. This function includes negotiating terms, pricing, and formalizing agreements. Service providers handle sales directly, but brokers or cooperative arrangements can facilitate this function by representing groups of producers.
-
Distribution is the process of coordinating the availability of agribusiness services to producers across Hawaiʻi Island. This function includes the logistics of service provision, ensuring that services are accessible to producers regardless of their location or schedule. This function enables multiple distribution channels for services to reach producers, which may involve in-person consultations, online platforms, mobile service units, or partnerships with local organizations.
-
Service Delivery is the execution phase where agribusiness services are provided directly to producers. This function involves implementing the services as agreed upon, which may include on-site technical assistance, training workshops, consulting sessions, or remote support via digital platforms. Service providers carry out this function, often collaborating with extension agents, specialists, or technology providers.